Introduction: Why Do Consensus Mechanisms Matter?
Did you know that over 80% of cryptocurrency transactions today rely on consensus mechanisms for validation? These underlying technologies are critical for ensuring the security, decentralization, and integrity of blockchain networks. Two popular consensus mechanisms, Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), dominate the landscape, while Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is gaining traction. In this article, we explore how these mechanisms work and their implications for the future of digital currency trading.
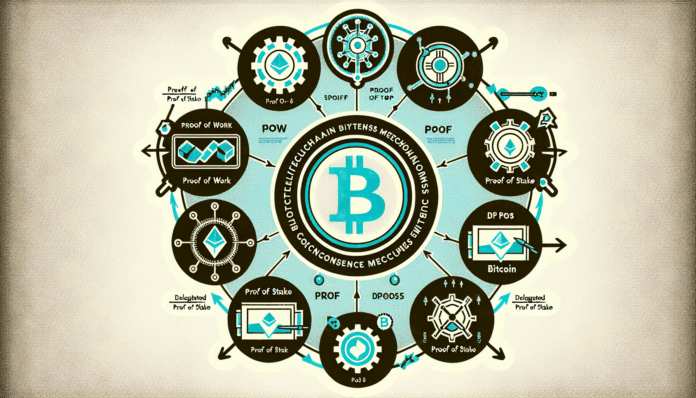
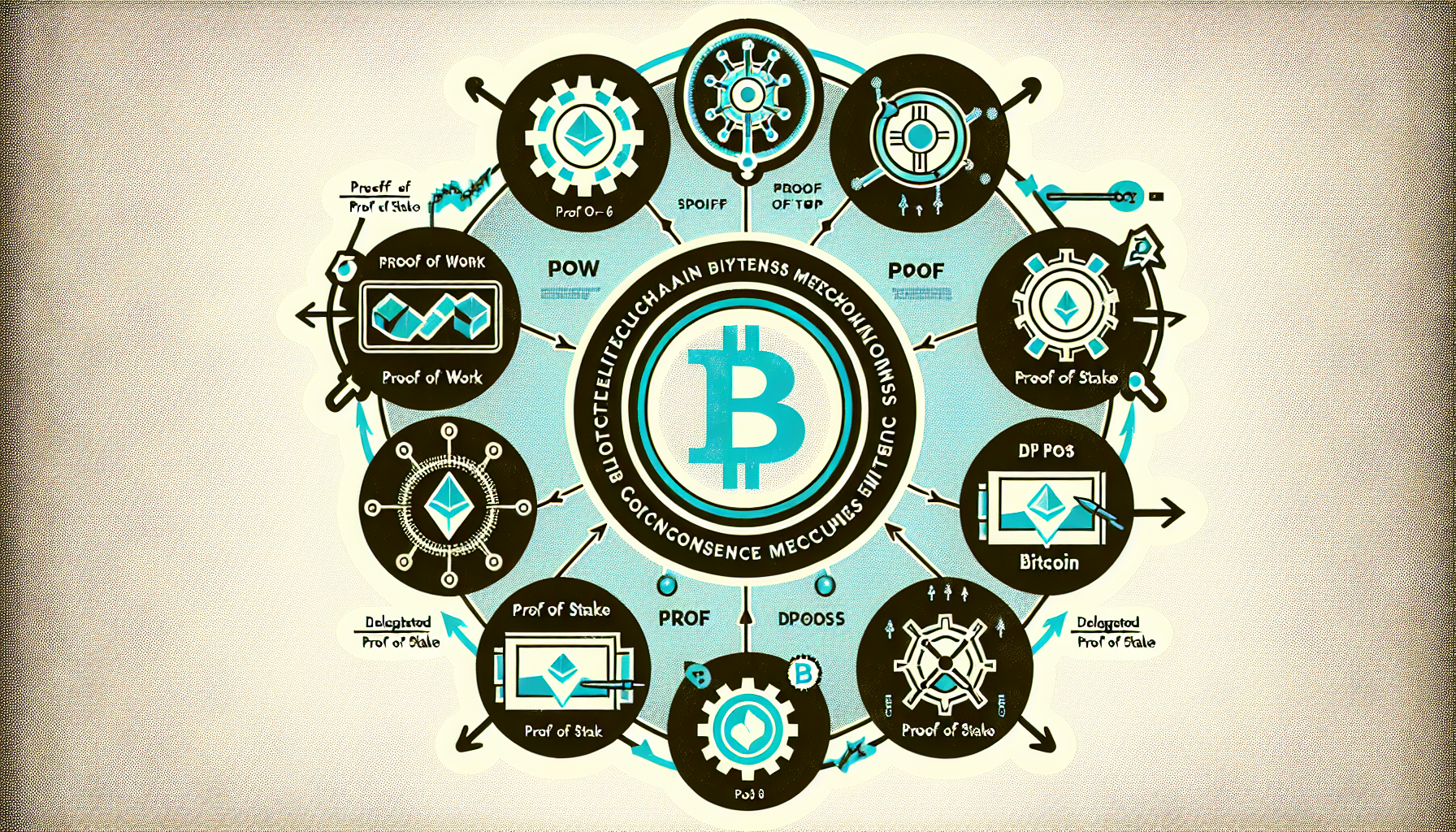
What is a Consensus Mechanism?
A consensus mechanism is a protocol that considers a transaction as valid when it is confirmed by all participants in the network. It ensures that all copies of the blockchain are the same and that any data entered is secure. Here’s how each type works:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions, requiring significant computational power and energy.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Participants, or validators, are chosen to add new blocks based on their existing stake in the network, making it more energy-efficient.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Users elect a small number of delegates to secure the network and validate transactions, enhancing efficiency and scalability.
How PoW Powers Leading Cryptocurrencies
Example: Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, uses PoW to secure its network. In PoW, miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles. The first to solve the puzzle validates the new block and adds it to the blockchain. While this ensures high security, it also leads to criticism due to its high energy consumption, estimated to consume more than 0.5% of the world’s energy supply.
The Advantages of Proof of Stake
With the rise of environmental concerns, Proof of Stake (PoS) has emerged as a popular alternative. Networks like Ethereum 2.0 are transitioning from PoW to PoS. This shift could reduce the energy consumption associated with validating transactions by over 99%.
In PoS, validators are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to